Getting Started
This guide covers the essential workflows for setting up and using KiLM (KiCad Library Manager), a command-line tool for managing KiCad libraries across projects and workstations.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- KiCad 6.x or newer: Must be run at least once to generate configuration files
- Python 3.9 or newer: Required for KiLM installation and execution
- Git: Optional, but recommended for library version control and collaboration
- KiLM: Install KiLM using pip, pipx, or uv
CLI showcase
Section titled “CLI showcase”A quick visual tour of the CLI experience:
1) kilm
Section titled “1) kilm”
2) kilm --help
Section titled “2) kilm --help”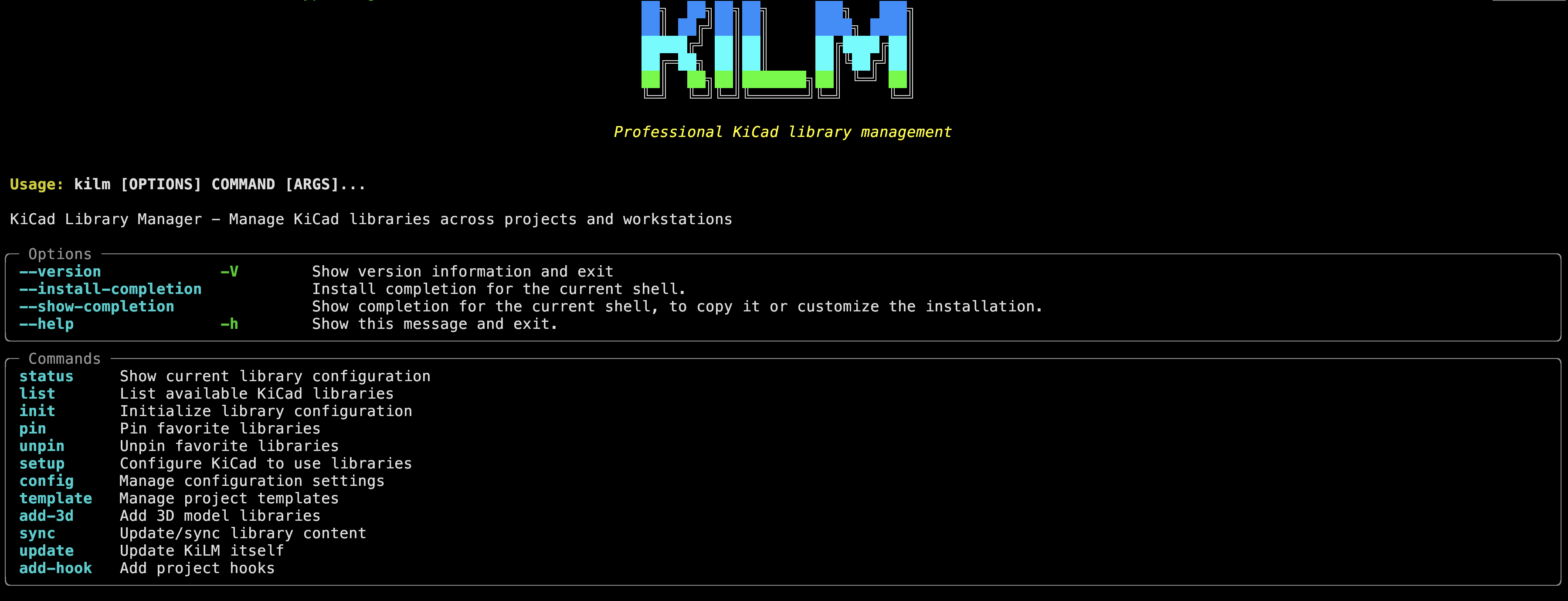
3) kilm config list -v
Section titled “3) kilm config list -v”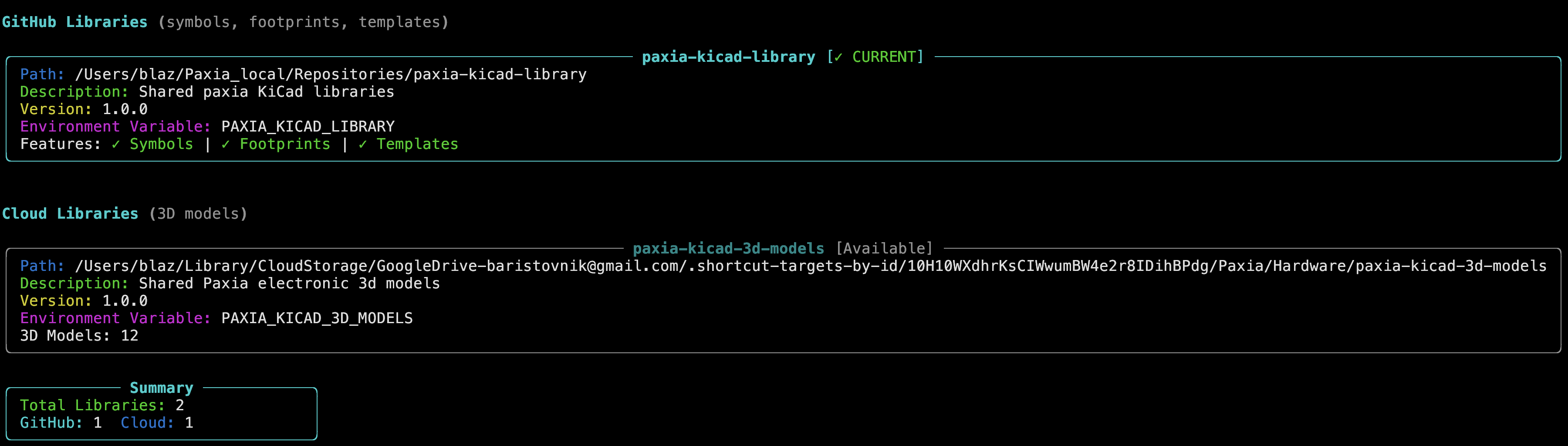
4) kilm sync
Section titled “4) kilm sync”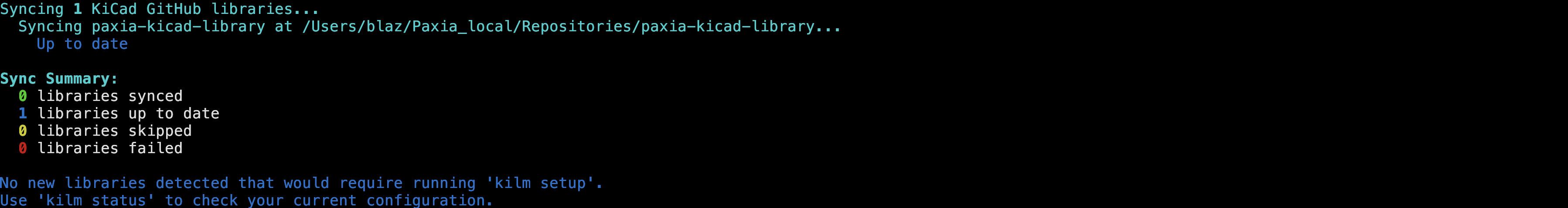
Understanding User Roles (Creator vs. Consumer)
Section titled “Understanding User Roles (Creator vs. Consumer)”KiLM is designed for teams or individuals managing KiCad libraries. We can think of two main roles:
- Creator: This person is responsible for setting up the central library structure (often in a Git repository), adding symbol/footprint libraries, configuring 3D models (which might be shared separately), defining custom metadata using KiLM, and potentially creating project templates. They establish the shared standard.
- Consumer: This person primarily uses the libraries set up by the Creator. Their main goal is to easily configure their local KiCad installation to use the shared libraries and keep it updated.
While one person might perform both roles, understanding this distinction helps clarify which commands are most relevant.
Typical Creator Workflow (Setting up a Shared Library)
Section titled “Typical Creator Workflow (Setting up a Shared Library)”This workflow assumes the Creator is setting up a new library repository to be shared with Consumers via Git.
-
Create and Navigate to Library Directory: Create a new directory for your shared KiCad library. This will become the Git repository.
Terminal window mkdir my-shared-kicad-libcd my-shared-kicad-libgit init # Initialize Git repository -
Initialize KiLM with Metadata: Run
kilm initinside the library directory, providing all relevant metadata. This creates thekilm.yamlfile which stores the canonical information for this library and gets committed to Git.Terminal window # Example: Initialize with name, description, and environment variablekilm init --name shared-company-lib \--description "Main KiCad library for ACME Corp" \--env-var ACME_LIB_PATH -
Add Library Content: Add your KiCad symbol (
.kicad_sym), footprint (.pretty), and other library files into the appropriate subdirectories withinmy-shared-kicad-lib. -
Register Shared 3D Models (Optional but Recommended): If you have 3D models stored in a shared location (e.g., Google Drive, network share), register this location with KiLM using
kilm add-3d. This adds the 3D library information to the Creator’s global KiLM config (config.yaml). Consumers will run a similar command later.Terminal window # Example: Registering a shared 3D model directorykilm add-3d --name shared-3d-models \--directory /path/to/shared/google-drive/kicad-3d-models \--env-var ACME_3D_MODELS -
Create Templates (Optional): If you want to provide standardized project starting points, use
kilm template make.Terminal window # Example: Create a template named 'standard-board' from an existing projectkilm template make standard-board /path/to/example/project --description "Standard ACME Board Template"Template files will be stored within the
templates/directory in your library repository. -
Commit and Push: Add all the files (
kilm.yaml, symbols, footprints, templates) to Git, commit, and push to the shared remote repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab).Terminal window git add .git commit -m "Initial library setup with KiLM metadata and content"git push origin main -
Configure Creator’s KiCad (Optional): The Creator can run
kilm setupto configure their own KiCad installation, just like a Consumer would.Terminal window kilm setup
Typical Consumer Workflow (Using a Shared Library)
Section titled “Typical Consumer Workflow (Using a Shared Library)”This workflow assumes a Creator has already set up a shared library in a Git repository.
-
Clone the Library Repository: Get a local copy of the shared library.
Terminal window git clone <repository_url> my-shared-kicad-libcd my-shared-kicad-lib -
Register Local Library Path with KiLM: Run
kilm initinside the cloned repository directory. This reads thekilm.yaml(created by the Creator) and registers this specific local path (my-shared-kicad-lib) in your global KiLM configuration (config.yaml), linking it to the name and metadata defined by the Creator.Terminal window kilm init -
Register Local 3D Model Path: Run
kilm add-3dpointing to the location where you access the shared 3D models (e.g., your local Google Drive sync folder). Use the same--nameand--env-varthe Creator used (check documentation or ask the Creator).Terminal window # Example: Pointing to your local path for the shared modelskilm add-3d --name shared-3d-models \--directory /Users/myuser/GoogleDrive/kicad-3d-models -
Configure KiCad: Run
kilm setupfrom anywhere in your terminal. This reads your KiLM configuration (which now includes the local paths registered in steps 2 & 3) and updates your KiCad’s library tables and environment variables.Terminal window kilm setup -
Set Up Automatic Updates (Optional, Recommended): Navigate to the directory of a specific KiCad project that uses the shared library (this project might also be a Git repo, potentially using the library repo as a submodule). Run
kilm add-hookhere.Terminal window cd /path/to/my/kicad-projectkilm add-hookThis sets up a Git hook in the project repository so that after you run
git pullin this project, it automatically runskilm setupfor you, ensuring KiCad stays synced if the library was updated.